Representation of Continuous Data
Representation of Continuous Data: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Grouped Data, Cumulative Frequency Distribution, Grouped Frequency Distribution Table, Cumulative Frequency Polygon, Histogram of Grouped Data, Frequency Density Histogram and, Ogive: Cumulative Frequency Curve
Important Questions on Representation of Continuous Data
A _____ is a zig-zag line that is usually drawn in the axis when the scale on the axis does not start from zero.
In histogram, the _____ of each bar represents the value whereas in bar chart the _____ of each bar represents the values that they represent.
Pie graph is used to represent data in continuous elements.
Which graph is used to represent data in continuous elements?
A railway line monitored of its August train journeys to find their departure delay times. The results are shown below. It is given that of these journeys were delayed by less than minutes.
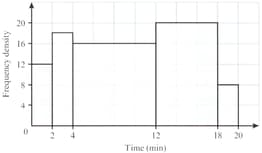
Find the total number of journeys provided in August.
A railway line monitored of its August train journeys to find their departure delay times. The results are shown below. It is given that of these journeys were delayed by less than minutes.
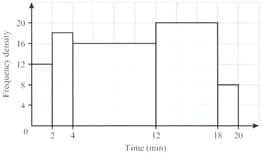
Calculate an estimate of the number of these journeys that were delayed by:
to minutes.
The masses, grams, of medical samples are given in the following table.
| Mass ( grams) | |||
| No. medical samples |
A shopkeeper takes bags of coins to the bank. The bags contain the following numbers of coins:
and
Each bag contains coins of the same value, and the shopkeeper has at least one bag containing coins with dollar values of and only.
What is the greatest possible value of all the coins in the bags?
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
The weights of sausages are summarised in the following table.
| Weight (grams) | |||||||
| Cumulative frequency |
State how many sausages weighed between and .
In a particular city there are buildings of historical interest. The following table presents the ages of these buildings, given to the nearest years.
| Age (years) | ||||
| No. buildings |
The densities, , of chemical compounds are given in the following table.
Find the frequencies and
| Density | ||||
| Number of compounds |
The densities, , of chemical compounds are given in the following table.
Find the frequencies and
| Density | ||||
| No. compounds |
The densities, , of chemical compounds are given in the following table.
Find the frequencies and
| Density | ||||
| No. compounds |
The densities, , of chemical compounds are given in the following table.
| Density | |||||
| No. compounds |
Find the frequencies and given in the table below.
| Density | ||||
| No. compounds |
